Diarrhoea
Everyone will be touched by diarrhoea at some point in their life. From the very old to the very young, no one gets to escape having loose, watery stools from time to time. … Read More See less
There are many different causes of a stomach ache and diarrhoea, most of which tend to clear up on their own within a few days. But whatever the reason for having diarrhoea, it’s a clear indicator that something in your body isn’t quite right, especially if you tend to have bouts of diarrhoea regularly.
Let’s explore what’s actually happening in your body when you have diarrhoea, the causes of diarrhoea and how to stop diarrhoea. Because no matter how common it is, it can be unpleasant and even distressing. So, let’s get to the bottom of it, together.
What is diarrhoea?
Diarrhoea occurs when your intestines push stools through before the bowel has absorbed excess water, which leads to loose, watery stools.1–3 It is defined by the World Health Organisation as 'the passage of three or more loose or liquid stools per day (or more frequent passage than is normal for the individual)’.4
Usually, it is mild and goes away on its own within a few days, but it can sometimes be a sign of something more serious.1 Based on how long it lasts, diarrhoea can be defined as:1,4
- Acute – less than two weeks of diarrhoea
- Persistent – more than two weeks of diarrhoea
- Chronic – more than 4 weeks of diarrhoea
When to see a GP for diarrhoea
You should arrange an appointment with your GP if you or your child:2,3
- Have had diarrhoea for more than three days
- Have severe pain in the abdomen or rectum
- Have a high temperature
- Have bloody or black and tarry looking stools
- Have signs of dehydration (e.g. fatigue, peeing less than usual, dry skin, feeling lightheaded or dizzy, dry mouth and thirst)
- Have sickness and diarrhoea at the same time
- Have stopped drinking fluids / are unable to keep fluids down
Diarrhoea symptoms
The signs and symptoms of diarrhoea include:1,2,5
- Loose, watery stools
- Cramping and abdominal pain
- Bloating
- A strong and urgent need to use the bathroom
- Nausea
- Headache
- Loss of water
Complications of diarrhoea
The biggest complication diarrhoea can cause is dehydration.1,7,8 This is particularly dangerous in children, people aged over 65 and those with weakened immune systems.1,7.8
If left untreated, dehydration can lead to kidney failure, stroke, heart attack or even death.1,7,8
Signs of dehydration include:2,3,5
- Fatigue and a lack of energy
- Peeing less than usual
- Dry skin
- Dry mouth
- Thirst
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy
- Sunken eyes
- Muscle cramps
- Rapid heartbeat
Symptoms of dehydration due to diarrhoea in infants and young children include:7
- Not having a wet diaper in three or more hours
- Having a dry mouth and tongue
- A fever above 39°C
- Crying without tears
- Sleepiness, unresponsiveness and irritability
- A sunken appearance to the belly, eyes or cheeks
Causes of diarrhoea
Acute diarrhoea is normally caused by gastroenteritis, due to an infection triggered by:2,3,5,8
- Viruses –g., norovirus, sapovirus and rotavirus
- Bacteria –g., Salmonella, Campylobacter jejuni, Shigella species, and Escherichia coli (E. coli). These are often spread through food-based sources
- Pathogens – g., protozoa including Cryptosporidium, Giardia, Entamoeba histolytica, and Cyclospora. These tend to contaminate water
Infections tend to thrive in areas with poor standards of public hygiene, meaning they often affect people who are travelling in developing countries.5,7
Acute diarrhoea can also be the result of:1,5,6
- Feelings of anxiety
- Drinking too much alcohol
- A food allergy (e.g. lactose or gluten)
- Medication (e.g. antibiotics and antacids)
- Surgery (e.g. gallbladder removal)
- Damage to the intestines due to radiotherapy
- Appendicitis
- Menstruation (if you have a condition that causes diarrhoea during menstruation, like endometriosis)
Chronic diarrhoea, however, is normally caused by disorders like:1,2,5,7–13
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) – regular episodes of bowel disturbance potentially caused by increased bowel sensitivity or abnormal muscle activity in the bowel wall
- Inflammatory bowel disease – a group of conditions, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, that occur when your immune system attacks your bowl
- Coeliac disease – a digestive condition caused by an inability to digest gluten
- Chronic pancreatitis – when the pancreas has become permanently damaged by inflammation and stops working properly
- Diverticular disease – where small bulges or pockets develop in the walls of the intestine (diverticular)
- Bowel cancer – cancer in the large bowel (including the colon and rectum), which can cause diarrhoea and bloody stools
- Gastrectomy – a surgical procedure to remove part of your stomach
How to treat diarrhoea
Most cases of acute diarrhoea will clear up on their own without any treatment, including diarrhoea caused by gastroenteritis.3,14
However, you should:3,14,15
- Drink plenty of water to replace any fluids lost and avoid dehydration
- Take paracetamol to help ease any stomach cramps or bring down a fever
- Get plenty of rest
- If you get diarrhoea after eating and are wondering what to eat when you have diarrhoea, you can try small amounts of plain foods like soup, rice, pasta and bread
- Use oral rehydration solutions made from sachets if you or your child have signs of dehydration
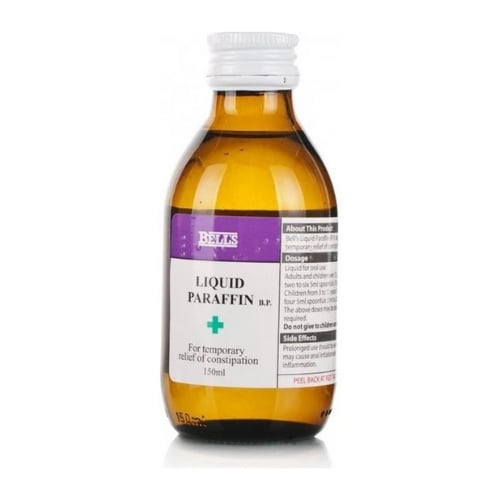
- Take diarrhoea tablets (loperamide) for short-term relief if you need to
If you have chronic diarrhoea, your GP will work with you to discover the cause.16 Treatment will therefore revolve around the cause of your diarrhoea.16 For example, if you have coeliac disease, you will need to follow a strict gluten free diet.17
How to prevent diarrhoea
As diarrhoea is often caused by an infection, you can reduce your risk of getting it by:1,3
- Washing your hands thoroughly with soap and warm water after going to the toilet and before eating or preparing food
- Cleaning the toilet, including the handle and the seat, with disinfectant after each episode of diarrhoea
- Avoiding sharing towels, flannels, cutlery, or utensils with other members of your household
- Storing food properly and cooking it to the correct temperatures
- Avoiding untreated tap water when travelling abroad
- Avoiding raw or undercooked food when travelling abroad
- Getting vaccinated for illnesses that can cause diarrhoea, such as rotavirus and COVID-19
Sources
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4108-diarrhea
- https://www.wsh.nhs.uk/CMS-Documents/Patient-leaflets/UpperGastrointestinalService/5151-3-Diarrhoea.pdf
- https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/stomach-liver-and-gastrointestinal-tract/diarrhoea/
- https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/diarrhoea-adults-assessment/background-information/definition/
- https://www.uhs.nhs.uk/Media/UHS-website-2019/Patientinformation/Generalmedicine/Diarrhoea-1360-PIL.pdf
- https://www.keepingwellnwl.nhs.uk/self-help-resources/womens-health/endometriosis
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diarrhea/symptoms-causes/syc-20352241
- https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/diarrhoea-adults-assessment/background-information/complications/
- https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/diarrhoea-adults-assessment/background-information/causes/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/inflammatory-bowel-disease/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/chronic-pancreatitis/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/diverticular-disease-and-diverticulitis/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/bowel-cancer/
- https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/stomach-liver-and-gastrointestinal-tract/gastroenteritis/
- https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/loperamide/about-loperamide/
- https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/diarrhoea-adults-assessment/management/chronic-diarrhoea-more-than-4-weeks/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/coeliac-disease/

Free delivery when you spend over £39
100% discreet delivery for every item ordered

Fully regulated UK pharmacy
Are there medicines for diarrhoea in children or infants?
Over the counter medicines to stop diarrhoea are usually suitable for children aged 12 and over, and should not be given to young children or infants.
If your child or baby has diarrhoea, we recommend speaking to your doctor for advice and a suitable treatment.
It’s important to make sure that your child doesn’t become dehydrated if they have diarrhoea, so make sure to give them sips of water, an energy drink, or an ORS drink often until their symptoms pass.
Can Buscopan products be used to treat diarrhoea?
Buscopan products are used to treat stomach cramps caused by IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome), your menstrual cycle, or other medical conditions.
Although diarrhoea and stomach cramps can often happen at the same time, Buscopan isn’t a recommended treatment for diarrhoea.
If you are unsure about which treatment or medication is right for you, we recommend speaking to your doctor or pharmacist for advice.
Can vitamin supplements cause stomach pain or diarrhoea?
Vitamin supplements usually won’t cause stomach problems like pain, nausea, or diarrhoea.
However, it’s important to note that supplements can have side effects sometimes, and stomach issues can be some of these.
This can happen if you’re sensitive or allergic to any of the ingredients in your supplement or simply because the supplement isn't right for you.
If you experience any side effects after taking a vitamin or supplement, you should speak to your doctor or pharmacist right away and ask for their advice.
What is the best diarrhoea treatment?
If you want a diarrhoea treatment that works quickly, try an over-the-counter product like loperamide (Imodium) or Pepto-Bismol.
Antibiotics may be given if it’s caused by a bacteria or parasite which you may have gotten from consuming food or water that’s been contaminated.
Diarrhoea that’s caused by a viral infection cannot be treated with antibiotics - you may want to try treatments at home, like eating bland foods, taking probiotics and drinking rice water.
What causes travellers’ diarrhoea?
Travellers’ diarrhoea is caused by drinking or eating food that contains bacteria, viruses and parasites.
You can prevent yourself from getting diarrhoea whilst travelling by avoiding unsafe water, such as buying bottled water or boiling the water first.
Try to avoid eating raw fish, meat or vegetables, and don’t put ice in your drink.
Why does vomiting and diarrhoea cause dehydration?
If you’re ill with a nasty stomach bug, frequent vomiting or diarrhoea can cause you to become dehydrated.
This is because your body is losing more fluids than it’s taking in, and it’s also losing essential salts and nutrients.
Your body needs water to function properly, so when you’re losing fluids through vomiting or diarrhoea you may start to experience symptoms like feeling thirsty, tired or dizzy.