Eczema & Dermatitis
Ever found your concentration waning because of a growing itchy feeling on the back of your knees, elbows, face or hands?[1] The urge to scratch is undeniable, but you know that doing so will only make it worse. If this description resonates with you, chances are you’ve struggled with eczema and/or dermatitis. … Read More See less
Eczema and dermatitis are extremely common conditions, affecting between 2–10% of adults and 10–30% of children[2]. And their prevalence is only growing. As a result, more and more people are looking to understand the underlying causes behind these conditions and what they can do to soothe their flare-ups.
Because as random as eczema and dermatitis flare-ups can seem, it becomes easier to identify what causes your eczema flare-ups when you understand your triggers. Keep reading to find out everything you need to know about eczema and dermatitis, including how they can be treated effectively.
What are eczema and dermatitis?
Eczema is the collective name for a group of inflammatory skin conditions, including atopic dermatitis, that cause your skin to become dry, itchy and bumpy[3].
Eczema occurs as flare-ups in response to specific triggers[4].On average, these flare-ups can last for between one and three weeks. Though this depends on the type of eczema, the trigger involved and your individual immune response[5].
There are seven different kinds of eczema:
- Atopic dermatitis – the most common type of eczema, which causes dry, itchy skin, rashes and inflammation
- Contact dermatitis – termed ‘contact’ dermatitis because it is triggered by contact with an allergen, which causes inflamed, itchy skin
- Dyshidrotic eczema – triggers including stress, irritants and excessive moisture on the hands and feet, cause small, painful, itchy blisters on the edges of the fingers, toes, palms, and soles of the feet. As they heal, these blisters cause cracked, scaly skin
- Neurodermatitis – a patch of itchy skin that only gets worse the more you scratch it, leading to a vicious cycle. This type of dermatitis is triggered by stress or localised irritation
- Nummular eczema – round patches of itchy, inflamed or oozing skin, often triggered during the winter months or following a cut, insect bite or burn
- Seborrheic (seb) dermatitis – affects oily areas of the body, such as the scalp, face or upper chest. Sometimes known as “cradle cap” in infants, it causes greasy and inflamed skin and yellowish scaly patches
- Stasis dermatitis – poor circulation in your legs can lead to swollen, itchy skin that may become dry and scaly over time and even cause open sores
Importantly, while some types of dermatitis fall under the eczema umbrella, others, such as perioral dermatitis, do not.
On white skin, eczema tends to appear red in colour. However, eczema makes brown and black skin appear darker. This can make the condition difficult to identify in people with darker skin types as it’s not as obvious. Yet, children with darker skin are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis and six times more likely to develop severe eczema than children with white skin[6].
Eczema and dermatitis symptoms
The specific symptoms you have will depend on the type of eczema you have. As a result, an eczema flare-up can present with any of the following symptoms:
- Itchy skin
- Dry skin
- A rash
- Swollen, inflamed skin
- Discoloured skin
- Rough, leathery skin
- Scaly patches
- Oozing or crusting skin
- Blisters
How are eczema and dermatitis diagnosed?
Eczema and dermatitis can usually be diagnosed by your GP. They will examine the affected area(s) and ask you to tell them about your symptoms and your history of the condition. Based on this information, they may be able to diagnose the specific type of eczema you’re struggling with[7].
From here, either your GP or a pharmacist should work with you to try to determine what your triggers are. For example, you may be asked to keep a food diary and note down any flare-ups you have, to try to identify whether flare-ups tend to occur whenever you eat a specific food.
What causes eczema and dermatitis?
While the underlying cause of eczema is still unclear, you are more likely to have eczema if you have[8]:
- A family history of eczema
- An overactive immune system
- A weakened skin barrier (the protective outer layer of the skin)
Eczema can be triggered by[9]:
- Exposure to an irritant or allergen – being exposed to a substance you’re allergic to will cause your immune system to produce inflammation which can lead to eczema
- Stress – high levels of stress, anxiety or depression can lead to more frequent eczema flare-ups
- Temperature changes – seasonal and temperature changes, humidity, and extreme heat or cold can all trigger flare-ups
- Skin infections – when bacteria (e.g. via a staph infection) penetrates the skin barrier, it can trigger the immune system and cause a flare-up
- Hormonal changes – if you get periods, you may find your eczema is exacerbated in the days before you’re due to menstruate. Many people also find their symptoms get worse during pregnancy
Common allergens or irritants that can trigger eczema include:
- Foods – common food allergies include eggs, dairy and nuts
- Fabrics or clothing materials – wool, latex and synthetic fabrics
- Metals – chromium, cobalt chloride, copper, gold and nickel
- Pets and insects – pet fur, dust mites, cockroaches and insect bites and stings
- Environment – pollen, mould, damp and cigarette smoke
- Fragrances – perfumes, scented cosmetic products (e.g. soap, moisturiser) and detergents
How can eczema and dermatitis be treated?
While there is no cure for eczema, you can reduce your chances of experiencing a flare-up by avoiding your triggers as much as possible[10].
There are also treatments that can help you manage the condition:
Topical corticosteroids
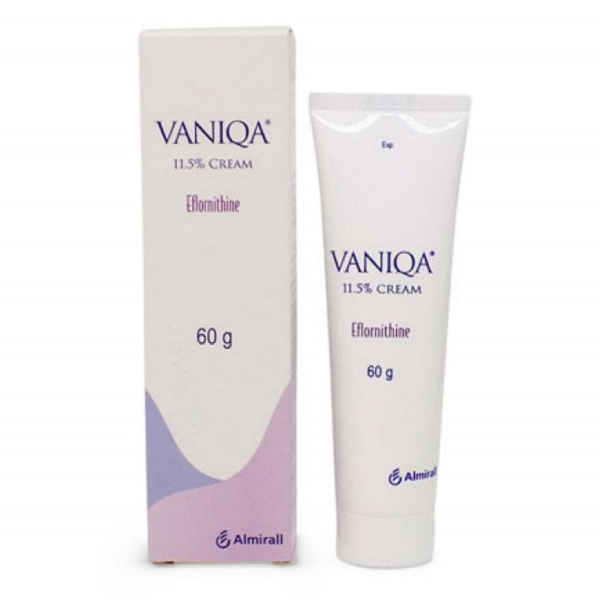
Topical corticosteroids are creams, lotions and gels that contain steroids, a group of hormones produced naturally by the body. For example, hydrocortisone cream, Eumovate and Betnovate. Topical corticosteroids can be used to reduce inflammation and speed up healing.
However, they should not be used around the eyes or on the face, on broken or infected skin, on the anal or genital areas, or by pregnant people. Additionally, hydrocortisone and Eumovate should not be used by anyone under the age of 10 and 12, respectively, with eczema. Newborns and babies, however, may be prescribed other topical corticosteroids, as they are a first-line treatment for babies with eczema.
Topical calcineurin inhibitors (TCI)
TCIs are eczema creams that block calcineurin, a protein that contributes to inflammation in atopic eczema. When applied to the skin, they can soothe the symptoms of a flare-up.
There are two types of TCI:
- Protopic ointment (tacrolimus) – for treating moderate to severe eczema. Protopic is available in 0.1% and 0.03% strength varieties
- Elidel cream (pimecrolimus) – for mild to moderate eczema
TCIs may be prescribed as an alternative to topical corticosteroids. For example, for use on delicate areas, such as the face and genitals.
Emollients
Emollients are unperfumed, medical moisturisers that soothe, moisturise and protect the skin. They work by adding an oily layer to the surface of your skin, which traps moisture beneath it to improve your skin’s hydration. It also helps to keep irritants and allergens from entering your skin, to prevent eczema flare-ups.
There is no best cream for dermatitis or best face lotion for eczema; however, there is only the cream, gel or lotion that works best for you. Just make sure you choose an emollient approved for use by the NHS. Some of these can be prescribed, but others can be bought over the counter.
Severe eczema treatments
If other treatments are not adequately treating your eczema, then you may need to speak to a dermatologist or your GP to see if they can provide you with a stronger treatment. These can include:
- Oral tablets – these calm the immune system and fight inflammation. They include abrocitinib, azathioprine, baricitinb, ciclosporin, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, tralokinumab, upadacitinib
- Injections – dupilumab is given as an injection and works by targeting specific proteins or receptors in the body to regulate the immune response
- Oral steroids – prednisolone is the most common oral steroid used in the UK. It works by suppressing the immune system
- Phototherapy – phototherapy uses ultraviolet light to reduce the number of T-cell lymphocytes in the skin, which are involved in the inflammatory response
Sources
- https://healthtalk.org/experiences/eczema/eczema-symptoms-what-does-eczema-look-and-feel-like/
- https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/eczema-atopic/background-information/prevalence/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9998-eczema
- https://nationaleczema.org/eczema/
- https://www.healthcentral.com/condition/eczema/how-long-does-eczema-last
- https://eczema.org/information-and-advice/living-with-eczema/skin-pigmentation/
- https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/skin-hair-and-nails/atopic-eczema/#diagnosing-atopic-eczema
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/atopic-eczema/
- https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/skin-hair-and-nails/atopic-eczema/#causes-of-atopic-eczema
- https://eczema.org/information-and-advice/living-with-eczema/skin-infections-and-eczema/

Free delivery when you spend over £30
100% discreet delivery for every item ordered

Fully regulated UK pharmacy
What is eczema?
Eczema is a skin condition that causes patches of skin to become dry, flaky, irritated and cracked.
It usually affects the front and back of knees and elbows, but it can occur on any part of the body.
Eczema tends to first occur in childhood and is a long-term skin condition that can cause discomfort, but some people find that they grow out of it as they get older.
Certain irritants and germs can cause symptoms of eczema to worsen, so it is essential that you keep your skin clean and hydrated.
There is no cure for eczema, but there are several steps you can take to help manage your skin:
- Moisturise your skin - use moisturisers, ointments or lotions that contain emollients to lock in moisture, prevent your skin from drying out and reducing the need to itch
- Avoid itching - itching the skin can cause germs to infect the skin, making symptoms worse
- Avoid long, hot showers/baths - hot water dries out the skin
- Use a soap substitute - harsh soaps can strip the skin of its natural moisture which can exacerbate symptoms of eczema
- Use an emollient bath oil - it will prevent your skin from drying out in bathing and can help to manage symptoms of eczema
If your eczema is severe speak to your doctor, who can prescribe a suitable treatment.
Are Childs Farm products safe for children with eczema?
Childs Farm products are designed to be suitable for people of all ages who have sensitive or eczema-prone skin, so they could be perfect for your child!
However, we always advise that people with eczema or sensitive skin perform a patch test 24 hours before using any new product.
To do this, apply a small amount of the product you’re testing to the inner part of your child’s elbow or behind their ear and let it dry, then cover the area with a bandage.
Keep the bandage in place for around 24 hours, and take care not to get the area wet.
If the area is clear after 24 hours, then you should be able to use this product without any problems.
However, if your child feels unwell or experiences any irritation in the area where you’ve performed the test, you shouldn’t use the product.
This will help to keep both you and your little one safe as you try to find a product that will help to soothe their eczema.
For more information about eczema, click the link below!
Can babies get eczema?
During your baby’s first few months, you may notice crusty or flaky patches on their skin which could be eczema.
If it is indeed eczema, babies with light skin will have patches of red skin and darker-skinned babies will have purple, brown or greyish patches of skin.
The patches of skin will be dry, rough and itchy, typically appearing on the cheeks and the joints of their arms and legs.
Eczema can affect just about any part of your baby’s body.
Can eczema be cured?
At this moment in time, atopic eczema can’t be cured, although I’m sure that many eczema sufferers (myself included) wish it could be!
However, you can try to avoid the irritants that cause your eczema and there are treatments available which can help to make your flare-ups more manageable when they do happen.
Some of the most popular treatments for eczema are creams and ointments, which can be applied to the area to hydrate your skin and reduce your symptoms.
How can emollients help me to manage dry skin and eczema?
Emollients and moisturisers help to ease your eczema symptoms by hydrating your skin, helping to keep your skin soft and controlling your flare-ups.
Emollients work by forming a protective layer over your skin which helps to keep moisture from escaping, hydrating your skin from the inside out.
Some emollients also contain ingredients which can protect your skin from irritants like soap or detergents, taking a two-pronged approach to managing your eczema flare-ups.
How can I treat eczema on my baby's face?
Your baby’s skin is delicate, especially on their face. To treat eczema on your baby’s face, use a gentle cleanser (we’d recommend the Aveeno Baby Range) and warm water to rinse, being careful to avoid their eyes, nose and mouth. Pat the face dry and apply a soothing, fragrance-free moisturiser. Although it’s unlikely your baby will be allergic to any of the skincare products, you should always test them on a small area on your baby’s skin beforehand.
How often should you shower with eczema?
When your skin isn’t clean, you’re more likely to have an eczema flare-up.
It’s recommended that you should shower daily to ensure that your skin is free from the day’s dirt and grime.
But what’s important is the time spent in the shower, the water temperature and the products used - as your skin is dry, you should use the ‘soak and seal’ method to trap in that much-needed moisture.
Where do people get eczema?
Eczema can break out anywhere on the body but it's most common in the following areas:
- Knees
- Elbows
- Neck
- Hands
- Cheeks
- Scalp
What bath additives are best for eczema or sensitive skin?
If you have eczema, dermatitis or another dry skin condition, you may find that taking a hot bath or shower dries out your skin, rather than hydrating it.
In these cases, we often recommend emollient bath oils, which form a protective barrier over your skin to keep moisture in and protect it from irritation.